Free up Disk Space. If you find that your RAM is completely full, but you’re still in need of storage, you can use free space on your Mac’s drive called virtual memory. This extra storage is found on Mac computer’s hard drives so that you can continue running apps.
When you use up all of the available RAM on your computer, you may notice that your device struggles to complete tasks. If you find that your computer’s applications are frequently crashing and it takes longer to do simple tasks, then you might be wondering how to free up RAM on your computer.
What is RAM?
Your computer’s Random Access Memory (RAM) is stored on a memory chip that is typically found on the motherboard. This where your computer stores short term data. RAM is the hub of storage for all active and running programs and processes. Your computer uses the information it has stored in RAM to complete tasks while simultaneously receiving and performing other functions.
When you use up all of the available RAM memory, your computer’s performance can slow down because it doesn’t have the storage required to complete its tasks. When you clear RAM space, it gives your computer the capability to carry out tasks. Depending on your computer, there are a few different ways you can free up RAM space.
- With CleanMyMac X installed on your system you will get a Heavt memory usage alert if your Mac is running out of free RAM. Just click on the Free Up button to release some of the RAM and speed. Click on the application icon, select 'Get info' from the 'File' menu, and adjust the memory allocation in the window that pops up.
- When memory usage reaches a critical threshold, your Mac will become sluggish or even completely unresponsive. When faced with this kind of a nuisance, try a few best-practice methods to reduce RAM consumption and give the system a productivity boost. Restart your Mac. Explore the Memory tab in the Activity Monitor and quit RAM-intensive processes.
- I have a MacBook Pro 2016, OS Sierra 10.12.5, 16gb memory. Starting about 1 week ago, I get the attached screenshot: The Force Quit box opens saying, 'Your system has run out of application memory'. Whatever application is open freezes and I have to force quit and restart. This happens with no rhyme or reason.
How to Make the Most of Your RAM
It can be easy to use up your RAM because it supports so many functions. Before you start removing programs from your computer, try these quick fixes to free up RAM space.
Restart Your Computer
The first thing you can try to free up RAM is restarting your computer. When you restart or turn off your computer, all of your RAM (stored data) will be wiped clean and programs will be rebooted. This can potentially clear out some processes and programs that are running behind the scenes, taking up your RAM storage.
Update Your Software
It’s important to be running the most updated versions of your computer software and applications. Older renditions of software and apps can take more memory to process, causing your computer to slow down.
Try a Different Browser
Something else you can try is changing browsers, as some have been known to use more data than others. If you’re not already, try using a browser like Chrome or Firefox, which are typically good browsers for memory management.
Clear Your Cache
If you still find yourself short on RAM, the next option is to try deleting your cache. Sometimes your cache can take up a lot of space because it uses RAM for memory functions. The cache holds on to information that your computer uses to reload pages it has seen before rather than downloading them again. This can save you time when browsing, but if you are short on RAM, it’s something you can sacrifice with minimal effect.
Remove Browser Extensions
Many of your daily work and home computer operations have been made easy by the use of browser extensions. However, they also require memory, so you might want to think about disabling or removing your extensions.
5 Ways to Free up RAM on Windows 10
If you are still having trouble freeing up your RAM storage, you might have too many programs and applications without even knowing. Try these five ways to free up RAM storage for Windows 10 computers.
1. Track Memory and Clean Up Processes
You should monitor your computer RAM usage so that you don’t deplete your supply before you really need it. To monitor your computer’s memory, you can navigate to the task manager to check the processes. This is where you’ll be able to see which programs are running and what kind of space they are taking up.
To locate your computer memory:
- Hold the Ctrl+Alt+Del keys to open the Task Manager.
- Select the “Processes” tab.
- Click the “Memory” column to view how much space they are taking up.
You can now see which of your programs are taking up the most time and space on your computer. If you find anything suspicious eating up your memory, you should delete programs you don’t need or use.
2. Disable Startup Programs You Don’t Need
If you have used your computer for at least a few years, then you have probably downloaded a fair amount of software that you either forgot about or no longer use. After the processes tab tells you which programs use the most space, you will want to maneuver to the startup tab to stop those you no longer need.
To disable startup programs:
- Select the “Startup” tab from the Task Manager.
- Click “Startup impact” to organize the programs from high to low usage.
- Right-click to disable any programs that you don’t need.
Startup programs are those that activate when your computer is booted up. When these programs start, each one takes up a little bit of RAM in the background without your consent. After a while, all of the software and programs can add up. Be sure that the ones that aren’t needed are disabled or removed.
How Do I Free Up Application Memory On My Mac
3. Stop Running Background Apps
The next items that could be taking up RAM are your applications that are set to automatically run in the background. You may have used your computer for years before noticing some of these apps taking up your RAM storage. This can quickly exhaust your memory, battery, and data bandwidth.
To stop background apps:
- Go to computer settings.
- Click the “Privacy” category.
- Scroll down the panel on the left side to “Background Apps.”
- Turn off any apps you do not use.
Applications are often automatically set to run in the background of your device. This enables them to display notifications and update their software automatically. By turning this off on apps you don’t use, you can save RAM storage.
4. Clear Page File When Shutting Down
When you restart your computer, your page files don’t get cleared or reset because unlike RAM, they get stored on the hard drive. So, when RAM gets stored on-page files it does not get cleared with the rest at shutdown.
Clearing page files on your hard drive will clear any RAM it has stored and help keep your computer running efficiently. You can set this to automatically clear when your computer shuts down, just like the RAM. Do this by opening the Registry Editor:
- Type “Registry Editor” into the start menu search bar.
- Click “Yes” to allow Registry Editor to make changes to your device.
- On the left, scroll to and select “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.”
- Scroll to select “SYSTEM.”
- Select “CurrentControlSet.”
- Find and select “Control.”
- Scroll to select “Session Manager.”
- Look for and choose “Memory Management.”
- Select “ClearPageFileAtShutdown.”
- Enter the number “1” under the value data and hit OK.

5. Reduce Visual Effects
With improving technologies, there are many more possibilities for computer effects and visuals. For example, you can turn off the animations for apps and icons that use storage for unnecessary effects. If you seem to be running low on RAM storage, there are some effects you can shelve until you free up more memory.
To access your computer’s visual effects:
- Open your File Explorer.
- Right-click on “This PC” on the left-side panel to select properties.
- Click “Advanced system settings” on the left.
- Select the “Advanced” tab.
- Choose settings under the “Performance” category.
- Change to “Adjust for best performance.”
This setting will disable all animated features on your computer. This will create more storage for you, but limit your computer’s aesthetics significantly. However, you can also customize which visual effects your computer will perform to your preferences in the same tab.
5 Ways to Free up RAM on Mac
For Mac users, there are many convenient tools to monitor and free up RAM storage on your computer.
1. Fix the Finder (Close Finder Windows Too)
How Do I Free Up Memory On My Mac Mini
When you open a new window in the finder, the data each window displays gets stored as RAM. Adjusting the finder preferences can make your folders open in tabs rather than new finder windows.
To open your Finder Preferences:
- Click “Finder” in the top left of your screen.
- Right-click on “Preferences” from the dropdown options.
- Check to Open folders in tabs instead of new windows.
There is another way to clear RAM storage by merging your Finder windows. To do this you will select the “Window” dropdown rather than Finder. From there you will select “Merge All Windows” to put all your Finder windows into one place. This will save you on storage as well as declutter your desktop.
2. Check Activity Monitor
To keep track of your RAM usage on Mac you can check the Activity Monitor, which shows you how much memory is being used and what is using it. Utilize the Activity Monitor to determine which apps take up most of your storage. Remove the ones you no longer use.
To Check the Activity Monitor:
- Search “Activity Monitor” in the spotlight search bar (command + space).
- Click on the “Memory” tab.
- Remove unwanted applications.
3. Check CPU Usage
You can also use the Activity Monitor app to check your CPU health and usage. CPU is your Central Processing Unit, and it carries out instructions from the computer software information stored as RAM.
To monitor your CPU, just select the “CPU” tab in front of the memory tab. This is where you can see if any apps take more processing power than others.
4. Clean-Up Programs and Applications
If you are looking to keep a consistently healthy amount of RAM storage, then you will want to keep your computer clean and organized. A cluttered desktop is going to use storage much faster because macOS views each desktop icon as an active window. Even if you don’t think you can organize your files, putting everything into one general folder can free up a lot of RAM.
5. Free up Disk Space
If you find that your RAM is completely full, but you’re still in need of storage, you can use free space on your Mac’s drive called virtual memory. This extra storage is found on Mac computer’s hard drives so that you can continue running apps. The function is always on, however to use virtual memory you will need to be sure you have driver space available to swap.
Additional Ways to Free up RAM on Windows or Mac
The best thing to do is to be proactive with your computer’s RAM so that you don’t have to worry about freeing up space. Use these additional ways to keep your RAM storage free.
Install a Memory/RAM Cleaner
If you find that you do not have the time, or you just cannot manage to organize your computer, there are memory cleaner apps to help you disinfect your computer. Many of these cleaners have special features for removing apps or extensions and allow users to manage their startup programs.
Increase RAM
You can always add more RAM to your computer if you have a lot of information you don’t want to delete. Buying and installing RAM is easy to do for a desktop computer, but can be troublesome for laptops. Be sure that you invest in the correct type of RAM for your computer as well as the correct amount for your specific storage needs.
Scan for Virus and Malware
When you download any software programs or extensions to your computer there is the chance they could have a virus or malware attached. Once you have malware on your computer, it can steal both your information and your RAM space. To prevent picking up any malware or viruses try using Panda Security antivirus to protect your computer and memory.
Now is the time to stop file hoarding. Many of the files on your computer are taking up RAM space without you realizing it. Now you know how to safely declutter your computer of these unused files and how to free up RAM so your computer runs more efficiently.
Sources: ComputerHope | WindowsCentral | HelloTech | DigitalTrends
MacBook storage issue is still a relevant one in 2021. The promised 1 TB of storage — which is the capacity of the MacBook Air 2020 — will still be not enough for many. We generate more and more content on our devices and use apps that are bursting with cache files. This is what creates the cryptic category of “Other” storage on Mac.
On recent macOS versions, this storage category is labeled “other volumes in container.” Which, of course, doesn’t make it any less cryptic. This category contains junk files as well as important ones. That’s why you have to learn to check the storage on Mac properly.
So let’s figure out what Other Storage is and how to remove Other from your Mac.
What is Other on Mac Storage?
Simply, Other storage on Mac consists of files that do not easily fall into the clearer category labels like 'Audio.' The types of 'Other' files would include:
- Documents like PDF, .psd, .doc, etc.
- macOS system and temporary files.
- Cache files like user cache, browser cache, and system cache.
- Disk images and archives like .zip and .dmg.
- App plugins and extensions.
- Everything else that doesn’t fit into the main macOS categories.
Like this file:

What’s this? A song? An unknown archive? Why on Earth does it weigh 200 MB?
How to check Mac disk space usage
A few years back, Apple introduced “Optimized Storage,” a great feature for finding out how your disk space is structured. This is how to check the storage on Mac.
- Open the Apple menu (top right corner)
- Now, click About this Mac > Storage
Is your disk approaching full capacity? Now, click “Manage.” The sidebar to the left is really enlightening. This is the only place where on your Mac, it shows the size of your apps, books, and documents in gigabytes.
Where is Other Storage on a Mac
To show you where it is, let’s look at your Library. This is where your macOS keeps application components, widgets, and various cache archives. This part of your Mac is hidden from view for a reason. Messing up a few folders here may break your Mac. But let’s take a look:
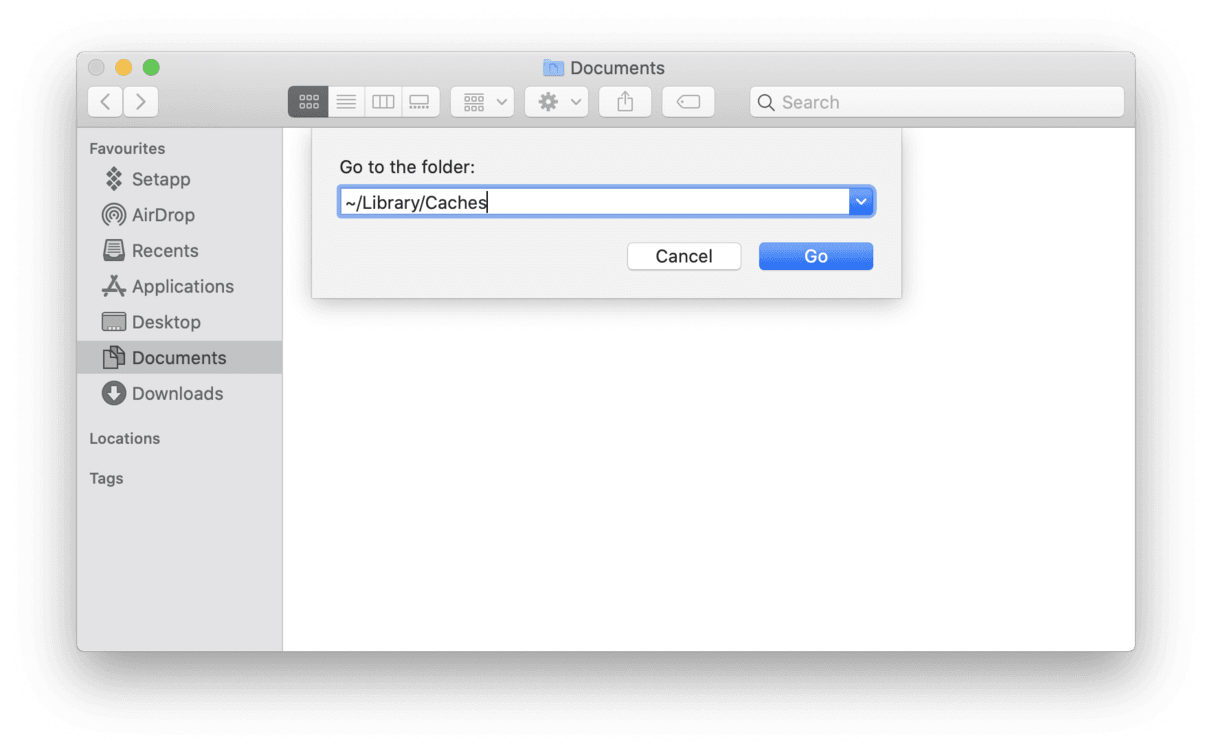
Click on Finder > Go (in the top menu).
Now paste in: ~/Library/Caches
See those small folders? This is where your “Other” storage is. You’ve found it. Now, we'll see what's possible to delete.
How to delete Other Storage on Mac
You can’t entirely get rid of Other on Mac, but you can reduce how much storage space it takes up. We’re now going to look at each of the six types of Other files and show you how to clean up your Mac. We’re going to walk you through deleting useless documents, junk system files, system slowing cache files, old backups, and all sorts of other junk.
1. Remove documents from Other Storage space
You might not think that pure text documents take up a lot of space, but you may be surprised at the size of some .pages and .csv files. And that’s before you start adding images, downloading ebooks, and creating big presentations. Soon your Other documents can start to get out of hand.
To find and remove large and unneeded documents from Other Storage manually:
- From your desktop, press Command-F.
- Click This Mac.
- Click the first dropdown menu field and select Other.
- From the Search Attributes window, tick File Size and File Extension.
- Now you can input different document file types (.pdf, .pages, etc.) and file sizes to find large documents.
- Review the items and then delete as needed.
Luckily, there’s a much quicker and more thorough way. By using a CleanMyMac X you are presented with a clear view of all the massive files occupying your Other space.
To locate large hidden files in all folders with CleanMyMac:
- Download CleanMyMac X and click the Large & Old Files tab.
- Click the big Scan button to start the search.
- Now, review the results broken down into different categories: archives, documents, movies, etc.
- Look through your files and delete the ones you no longer need.
What’s great about this method is that you can sort the files by their size and thus free up space most effectively. And there’s a special category for Other files that don’t fit into either category. CleanMyMac X also locates .DMG files and archives the Other storage often comprise. These files can be moved to another folder/separate disk or could be removed securely.
Now, try it and see how it helps you slim down Other storage on Mac. Deleting your old files alone can recover you tons of space, but there are more space hoggers that fall under the Other data category.
2. Clean up Other space of the system and temporary files
Every second your Mac is on, the macOS creates and piles up system files — logs, for example. At some point, the system needs these files, but they quickly become outdated and just sit there, wasting your disk space. And guess what, they are in the Other Mac storage category, too.
These files are mostly temporary, but they never actually go away unless you do something about it. The difficulty is that Apple hasn’t made it easy to clear out system files. There’s a good reason for this – people often delete things they shouldn’t.
Let's inspect your Library folder
To manually find where a majority of apps temporary files live, navigate to ~/Users/User/Library/Application Support/. In this folder, you will find your applications, and some searching will reveal a lot of space being taken up. For example, you may have gigabytes worth of old iOS backups in ~/Library/Application Support/MobileSync/Backup
You could delete these manually, but a much safer and faster method is to use a specialist cleaning app like CleanMyMac X. It has a System Junk module that specifically looks for useless system files and knows what’s safe to delete.
Here’s how to easily remove system files from Other Storage:
- Go to System Junk in CleanMyMac X.
- Hit Scan.
- Hit Clean.
That’s pretty much it. Seriously. If this is the first time you ever cleaned your Mac, you’ll see that the OS X Other storage tab has shrunk considerably after the system junk cleanup.
Using this method, I also deleted 16.69 GB of 'System Junk' from my MacBook.
3. Delete cache files from the Other data section
Cache files are not just another invisible storage hog. They are often one of the worst offenders, often taking up gigabytes of precious space. The three main types of cache are – browser, user, and system. Cache files are meant to help your system work faster, but they get bigger and bigger over time, eventually slowing your system down.
To manually clear cache files on Mac:
- Navigate to Go > Go To Folder.
- Type in
~/Library/Cachesand click Go. - Click-hold Option and drag the Caches folder to your desktop as a backup in case something goes wrong.
- Select all the files in the Caches folder.
- Drag them to the Trash.
- Empty Trash.
Follow the same steps for /Library/Caches (without the “~”) and ~/Library/Logs. Cache files sit in numerous folders, and with a little patience, you can clean them out manually (read more detailed instructions on clearing cache).
How Do I Free Up Application Memory On My Mac
4. Remove app plugins and extensions from Other storage
Another cool way to manage storage on Mac.
While apps are, unsurprisingly, categorized as Apps on the Storage bar, their add-ons are under the Other storage category. Compared to some types of files, app plugins and extensions probably won’t take up as much of your Mac's Other space. Still, every bit counts. Since extensions can sometimes cause other problems on your Mac, why not remove the ones you don’t use to be safe and free up some extra Other storage space at the same time?
Tracking down all your add-ons can be a hassle. Some you’ve forgotten you had (like that nCage extension for Chrome), others you didn’t know of in the first place.
Here’s how to manually remove extensions from Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
To remove extensions from Safari:
- Open Safari browser.
- Go to the Safari menu and click Preferences.
- Select the Extensions tab.
- Select the extension you want to remove and click “Uninstall.”
To remove extensions from Chrome browser:
- Open Chrome.
- Click the three-dot icon in the top-right corner.
- Click More tools > Extensions.
- Disable or remove as you choose.
To remove extensions from Firefox:
- Open Mozilla Firefox browser.
- Click on the burger menu in the top-right corner.
- Choose Add-ons.
- From the Extensions and Plugins tabs, disable and remove whatever you want.
Important! If you’re not sure what a plugin does, don’t rush to remove it. Try disabling it first and see if your apps and your system work as expected. You can always remove that add-on later. Also, note that Chrome extensions can’t be deleted automatically. But if you’d like to get rid of them, we’ll list these extensions for you and tell you how to do that manually.
5. Clear Other space of disk images and archives
Normally, archives and images are files you keep for a reason. However, if you think you might have accumulated some useless .zip and .dmg files on your Mac, then you should definitely clear them out as well.
You can find these files using Spotlight search:
- Open Finder.
- Type DMG/ZIP in the search field.
- Select Search: This Mac.
- Sort the results by Size.
Finder will show you all files of the format you’ve specified, sorted by size. You can clean out those you don’t need.
To safely and easily remove all your old unused disk images, CleanMyMac X has a dedicated tool within the System Junk module. Everything is categorized, so you have a better understanding of what you’re removing.
- Go to the System Junk module in CleanMyMac X.
- Click Scan and when it’s done, click Review Details.
Now you get a detailed overview of some ultra-specific categories of files that are normally invisible to you. Among those, you’ll see Unused Disk Images (another name for DMG installations). Then, there’s Old Updates — you would like to remove those too. Old Updates are past versions of update packages that you already got installed.
Do you often use graphic editors like Photoshop or Sketch? Then, you’ll probably be fascinated by the Document Versions feature. If you click on the Document Versions tab (System Junk > Scan > Review Details), you’ll be able to see how much of your space is taken by large document re-edits. Imagine a 60 MB Photoshop file cloned 10 times with just slight differences. In CleanMyMac X, you can delete these intermediate revisions. And, handy enough, the program keeps just the original file and its final revision on the drive.
6. Get rid of everything else from Other disk space
Even Other storage space has its own “other” files, and no, the irony of that statement is not lost on us.
Other storage on Mac can also include:
- Files in your user library (screen savers, for example).
- Files Spotlight search doesn’t recognize.
Typically, they won’t be as big of a share of Other data on your Mac as cache files and other items we’ve cleared out. However, if you’re determined to clean out as much Other Mac storage as possible, here’s how you can delete screensavers:
- Open Finder.
- In the Menu bar, select Go > Go to Folder.
- Type this:
/System/Library/Screen Savers/and click Go.
You’ll see the screen saver files now — they are lightweight, but for the sake of being thorough, you can trash them as well.
As for files, Spotlight doesn’t recognize, they are rare. They could include files like Windows Boot Camp partitions or virtual machine hard drives. If you don’t recall putting anything like that on your Mac, you probably have nothing to look for.
7. Remove application logs and support files
Apps on your Mac generate and store lots of files, which are mainly logs and support files. After you delete the application, those files lay still on your hard drive occupying space and doing nothing. So it’s a good idea to remove those.
- Open Finder.
- Press Command-Shift-G and go to
~/Library/Application Support
How Do I Free Up Application Memory On My Mac Free
Look for the folders that have the same name as the app you’ve deleted. You can safely move those to Trash.
Then, go to the following locations to delete other app-related files:
How To Clear Space On Macbook
~/Library/Logs
~/Library/Containers
And it's done! Hopefully, you managed to free up some GBs in the Other storage section.
How much can you expect to delete from Other storage on Mac?
How To Free Up Application Memory On My Mac
You’ll never remove the Other data section from Mac entirely, nor should you want to. It’s perfectly fine to have space taken up by necessary files, whatever category label they have. What is not okay is valuable storage space being wasted. Having a monthly cleanup can help you remove old, unneeded files and keep your hard drive organized.